Robotic and laparoscopic surgery for gallbladder stones is a minimally invasive approach designed to safely and effectively remove gallstones and relieve associated symptoms.
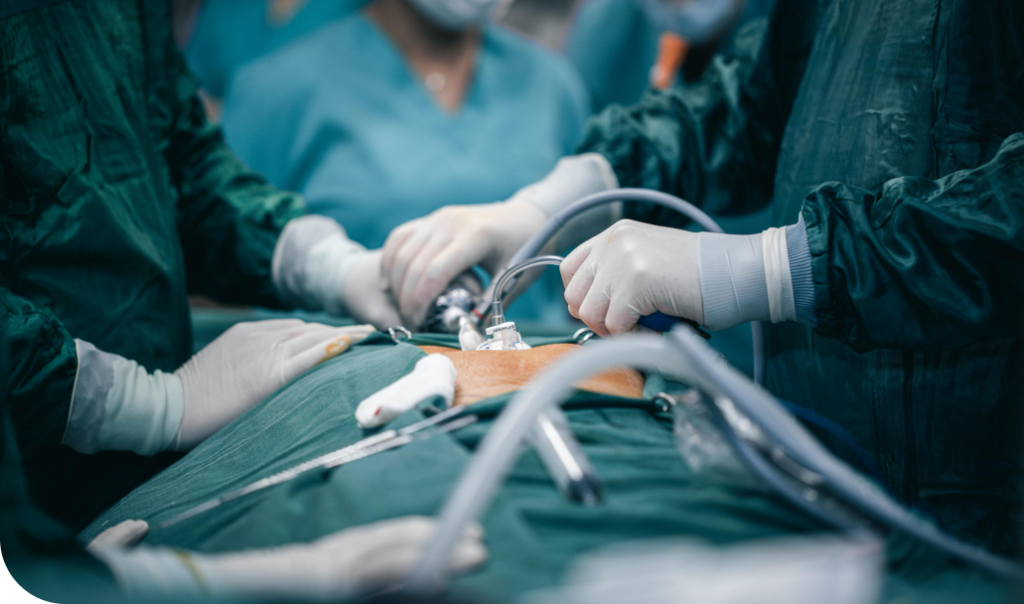
These advanced surgical techniques offer significant advantages over traditional open surgery, including reduced pain, faster recovery, and minimal scarring. By using cutting-edge robotic systems and high-definition laparoscopic technology, this procedure ensures precision and optimal patient outcomes.
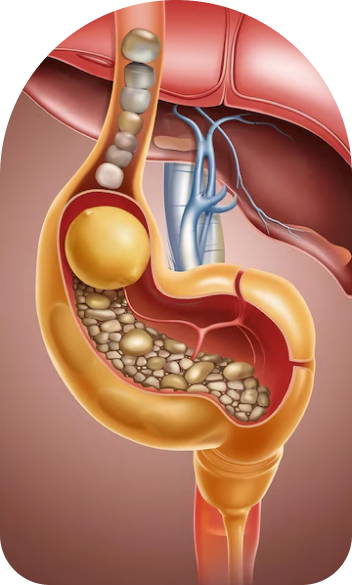
Possible causes of right upper abdominal pain include
Common causes of shoulder pain include
The standard treatment for a reducible hernia is surgery.

Possible causes of right upper abdominal pain include

Changes in weight can signal an abnormal function of the thyroid gland. Low levels of thyroid hormones .
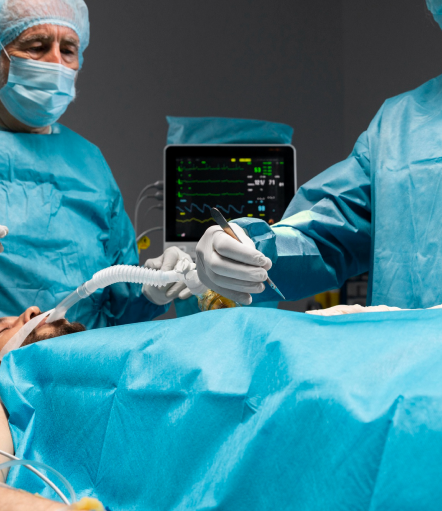
The standard treatment for a reducible hernia is surgery.
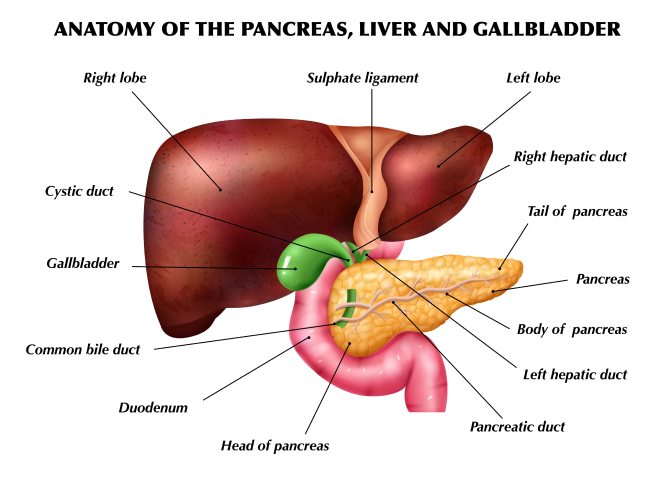
Gallbladder surgery, also known as cholecystectomy, is a procedure performed to remove the gallbladder. The gallbladder is a small organ located under the liver, responsible for storing bile, which helps in the digestion of fats. Gallbladder surgery is commonly done to treat conditions such as gallstones, gallbladder inflammation (cholecystitis), or other related problems.
This is the most common method for gallbladder removal. It involves making several small incisions in the abdomen, through which a tiny camera (laparoscope) and specialized surgical instruments are inserted. The surgeon uses the camera to guide the procedure, allowing for the removal of the gallbladder with minimal scarring.
Robotic and laparoscopic gallbladder surgery, also known as cholecystectomy, involves the following steps:
1. Pre-Operative Evaluation: Imaging studies such as ultrasound or MRCP confirm the presence of gallstones and assess the gallbladder’s condition.
2. Minimally Invasive Surgery: Small incisions are made, and a laparoscope or robotic tools are introduced.
3. Gallbladder Removal: The gallbladder is carefully detached from surrounding tissues and removed through one of the small incisions.
4. Closure: The incisions are closed with sutures or adhesive, leaving minimal scars. The procedure is performed under general anaesthesia and typically takes 1-2 hours.

"As a mother, it was worrying when my child was diagnosed with hypothyroidism at the age of 10. He had been feeling constantly tired, had trouble concentrating in school, and was gaining weight despite a healthy diet. After several tests, we learned that his thyroid was underactive, which was the cause of his symptoms.

Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam.
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.