Robotic/ Laparoscopic Solid Organ Surgery
Robotic and laparoscopic solid organ surgery offers unmatched precision, minimal invasiveness, and faster recovery compared to traditional open surgery. Using small incisions, these techniques reduce pain, blood loss, and scarring while ensuring optimal outcomes through enhanced visualization and meticulous dissection.
What is Laparoscopic Solid Organ Surgery?
Robotic and laparoscopic solid organ surgery represents a paradigm shift in contemporary surgical method. Combining state-of-the-art robotic with minimal invasive laparoscopic techniques, this paradigm shift allows unprecedented precision, shortened recovery time and the best solutions for patients with complex solid organ disease. Its combination of technological innovation and medical expertise has transformed the field of surgery, setting new standards in patient care and surgical success.
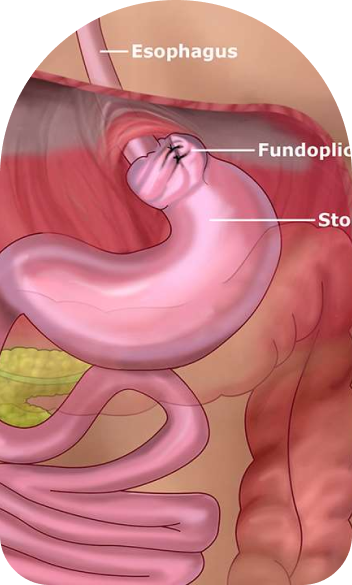
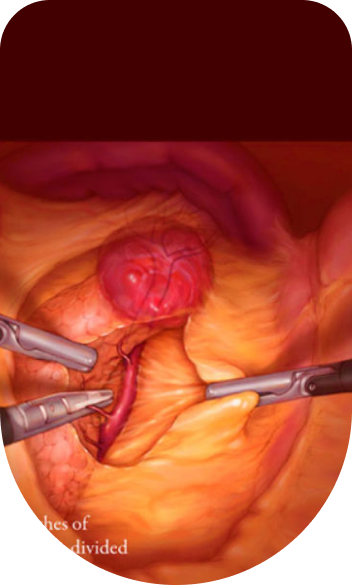
Symptoms Of Laparoscopic Solid Organ Surgery
Abdominal pain
Persistent itching or irritation around the anus, which may be caused by hemorrhoids or other anorectal issues.
Tenderness
A noticeable lump or swelling around the anus, which may indicate hemorrhoids or other growths.
Bleeding
Difficulty controlling bowel movements or leaking stool, often seen in cases of rectal prolapse.
Treatments
Surgery

Transplantations
Laparoscopic Solid Organ Surgery?
Endoscopic Anorectal Surgery is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat conditions affecting the anus and rectum, such as hemorrhoids, anal fissures, or rectal prolapse. This technique uses an endoscope, a thin, flexible tube with a camera, which allows the surgeon to view the affected area on a monitor
Surgery
Robotic and laparoscopic solid organ surgeries are meticulously planned and executed to ensure optimal outcomes with minimal invasiveness. The procedure begins with detailed pre-operative imaging, such as CT or MRI scans, to map the anatomy and plan the surgical approach. Under general anesthesia, small incisions are made to insert a laparoscope and robotic instruments. The laparoscope provides a magnified, high definition, three-dimensional view of the surgical site, enabling the surgeon to perform precise and delicate maneuvers from a robotic console. Using advanced robotic arms, the surgeon carefully excises or repairs the affected organ while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues. Once the targeted tissue is removed or the repair is complete, the excised specimen is retrieved through one of the small incisions for further analysis. The procedure concludes with meticulous closure of the incisions, ensuring rapid healing and minimal scarring. This innovative approach significantly reduces surgical trauma, leading to improved outcomes and faster recovery for patients.
- Pre-Operative Consultation A comprehensive review of the patients medical history, diagnostic tests, and imaging studies is considered an essential step.
- Medication Management Discontinuation of anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents, or other medications that may interfere with the surgery.
- Dietary Restrictions Fasting is typically required for 8–12 hours before surgery to prepare the body.
- Lifestyle Adjustments Patients may be advised to cease smoking or alcohol consumption to optimize healing and reduce surgical risks.

Srihas
"I had been suffering from hemorrhoids and persistent anal fissures for months, which caused discomfort and pain, especially during bowel movements. After consulting with my doctor, I was recommended to undergo Endoscopic Anorectal Surgery as a minimally invasive option to treat my condition.

Susan
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium, totam rem aperiam.
John
Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate velit esse cillum dolore eu fugiat nulla pariatur.